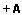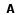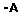Resumo: Para que o sistema de transporte público seja prestado com qualidade é necessário investigar e resolver inúmeros problemas, e dentre os problemas computacionais, existe o Problema de Escalonamento de Motoristas de Ônibus (PEMO), o qual é NP-difícil. Este trabalho apresenta quatro novos algoritmos da meta-heurística VNS para o PEMO, um GVNS e três VNS denominados adaptativos. Os quatro algoritmos possuem uma fase construtiva em comum e uma fase melhorativa que os diferem, tal que na fase melhorativa, os métodos Processo de Corte e Recombinação (PCR) e k-swap foram aplicados. Os algoritmos foram avaliados ao serem aplicados em instâncias da cidade de Maringá, PR. Na avaliação dos algoritmos propostos, foi constatado que todos são competitivos, pois eles geraram soluções melhores em relação à função de custo ao serem comparados à uma outra abordagem recente, tal que o melhor algoritmo proposto obteve melhores soluções na faixa de 4% a 14%. E em relação a um limite inferior o melhor algoritmo ficou na faixa de 12% a 25% acima desse limite.
Abstract: For the public transport system being provided with quality, it is need to tackle numerous problems and one of them is the Bus Driver Schedule Problem (BDSP) which is NP-hard. This work presents four new algorithms of the VNS meta-heuristic for the BDSP, one GVNS and three VNS named adaptatives. The four algorithms have a constructive common phase and an improved phase that differs them, such that in the improved phase, the Cut and Combine Process and k-swap were applied. The algorithms were evaluated applying them on instances of Maringá, PR, Brazil city. In the algorithm evaluations was found that all are competitive when they were compared with another recent approach, because they generated better solutions with respect to the cost function, such that the best algorithm obtained better solutions in the range of 4% to 14%. With respect to a lower bound the best algorithm got the range of 12% to 25% over this bound. |