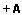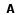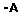Resumo: O gênero Capsicum compreende um rico gênero em aspectos morfológicos e genéticos. Estudos de diversidade genética ligada a este gênero são necessários para maior compreensão sobre as espécies, além de descobertas sobre novas informações em bancos de germoplasma de Capsicum. Este trabalho teve como objetivo analisar a variabilidade genética de três espécies do Capsicum (9 acessos) oriundas do Banco Ativo de Germoplasma da Universidade Federal do Piauí ? BAGC. Para isso, utilizou-se da técnica de eletroforese de isoenzimas em gel de amido para a análise de cinco sistemas isoenzimáticos (ACP, GPI, IDH, MDH e PGM). Foram detectados sete loci enzimáticos e 13 alelos, sendo que cinco alelos foram exclusivos, três presentes na população de C. annuum var. glabriusculum (Gpi(c), Idh(a) e Acp(b)) e os demais na população de C. baccatum var. pendulum (Pgm-1(b) e Pgm-2(b)). Todas as populações apresentaram loci polimórficos. O número médio de alelos por locus variou entre 1,4286 e 1. Os dados da estatística de Wright não foram compilados devido somente à presença de indivíduos homozigotos nas três populações analisadas. As identidades e as distâncias genéticas de Nei (1972) calculadas demonstraram uma diferenciação entre as espécies. O dendrograma de UPGMA construído demonstrou que as populações foram agrupadas em dois conjuntos: C. annuum var. glabriusculum+C. chinense e C. baccatum var. pendulum. Concluímos, portanto, que a diversidade genética dos acessos analisados é baixa e que os métodos utilizados nesta pesquisa são eficazes na diferenciação de espécies de Capsicum, comprovando assim a grande diversidade presente no gênero Capsicum.
Abstract: The genus Capsicum comprises a rich genus in morphological and genetic aspects. Studies of genetic diversity about this kind of genus are necessary to a further understanding about species, besides discoveries about new information in Capsicum germplasm banks. The objective of this study aimed to analyze the genetic variability of three species of Capsicum (9 accesses) coming from the Active Germplasm Bankof the Federal University of Piaui - BAGC. We used the technique of isozyme electrophoresis in starch gel for the analysis of five isozyme systems(ACP, GPI, IDH, MDH and PGM). As a result seven enzymatic loci and 13 alleles were detected, considering that, five alleles were exclusives, three were in the C. annuum var. glabriusculum (Gpi(c), Idh(a) and Acp(b)) sample, and the others were found in the C. baccatum var. pendulum (Pgm-1(b) and Pgm-2(b)) sample. All samples had polymorphic loci. The average number of alleles per locus varied between 1,4286 and 1. The statistical data of Wright was not compiled due to the presence of homozygotes in all three analyzed samples. The calculated identities and genetic distances of Nei (1972) showd a differentiation among the species. The constructed UPGMA dendrogram showed that the samples were grouped in to two sets: C. annuum var. glabriusculum+C. chinense and C. baccatum var. pendulum. Therefore we conclude that the genic diversity in the analyzes access in low and the methods used in this study are effective in differentiate species of Capsicum, proving the great diversity present in the genus Capsicum. |