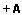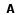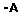Resumo: Avaliar a eficácia de diferentes instrumentos utilizados para o acabamento do término cervical de preparos protéticos. Quarenta e oito terceiros molares humanos extraídos com dimensões similares foram selecionados. Os dentes foram submetidos a preparos com finalidade protética com ponta diamantada em alta rotação apenas em parte de suas faces proximais e na face vestibular. Então, eles foram divididos em quatro grupos experimentais (n=12) de acordo com o método de acabamento do término cervical utilizado: Grupo 1 (Instrumento manual), Grupo 2 (Broca multilaminada), Grupo 3 (Ponta diamantada) e Grupo 4 (Ponta diamantada para Ultrassom). O acabamento foi realizado apenas em metade da face vestibular de cada dente. Após os procedimentos de acabamento, os corpos de prova foram submetidos à análise em Microscópio Eletrônico de Varredura (MEV). Focalizações padronizadas foram realizadas para todos os dentes no lado com acabamento e no lado controle (40x). As imagens foram organizadas em Microsoft PowerPoint 2010. Sete profissionais especializados na área foram selecionados para a avaliação dos términos cervicais das imagens classificando-as em: 1-ruim, 2-regular, 3-boa e 4-ótima. Esses mesmos profissionais tiveram contato visual com os espécimes e os avaliaram de acordo com o mesmo escore. As imagens também foram analisadas pela ferramenta de contagem de defeitos do Adobe Photoshop CC de forma quantitativa. Os dados da análise qualitativa foram analisados estatisticamente com o Teste de Friedman (p<0.05), enquanto os da análise quantitativa por análise de variância (ANOVA) e Teste de Tukey HDS (p<0.05). A análise qualitativa das imagens revelou melhores resultados para o grupo submetido ao acabamento com o Ultrassom (p<0.05). A análise visual confirmou a melhor eficácia do Ultrassom, com menor porcentagem de preparos considerados ruins (6.3%) e a maior porcentagem de preparos considerados ótimos (33.3%) quando comparado aos outros grupos. Quantitativamente o grupo 4 apresentou a menor média de defeitos e diferiu de forma estatisticamente significante do grupo 2 (p<0.05), que se apresentou com o maior valor médio de defeitos. Os grupos com e sem acabamento não diferiram de forma estatística entre si. Os procedimentos de acabamento podem interferir positivamente ou negativamente na regularidade da linha do término cervical. Os preparos mais regulares foram os que mantiveram uma ponta de mesmo formato da que foi realizada o preparo (Ponta diamantada e Ultrassom).
Abstract: Evaluate the effectiveness of different instruments used for polishing the finish line of prosthetic preparations. Forty-eight extracted third molars with similar dimensions were selected. Teeth were prepared for prosthetic treatment with a diamond tip at high speed handpiece only in the buccal surface. So, they were divided into four experimental groups (n=12) according to the method of polishing the finish line: Group 1 (manual instrument), Group 2 (multilayered bit), Group 3 (diamond tip) and Group 4 (diamond tip for Ultrasound). The polish was performed for only half of the buccal surface of each tooth. After the finishing procedures, the specimens were subjected to analysis in Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM). Standardized focalizations were performed for all teeth in the polish side and the control side (40x). The images were organized in Microsoft PowerPoint 2010. Seven specialized professionals were selected for the evaluation of the finish lines of the images using this classification: 1-poor, 2-regular, 3-good, 4-excellent. These same professionals have visual contact with the specimens and evaluated according to the same score. The images were also analyzed quantitatively with the counting defects tool of Adobe Photoshop CC. The qualitative analysis were statistically analyzed with the Friedman test (p<0.05), while quantitative evaluation by analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey HDS test (p<0.05). Qualitative analysis of the images showed better results for the group submitted to polishing with Ultrasound (Group 4). Visual analysis confirmed the effectiveness of the Ultrasound, with a lower percentage of poor preparations (6.3%) and the highest percentage of excellent preparations (33.3%) compared to other groups. Quantitatively, group 4 had the lowest mean defect and differed statistically significantly from group 2, who presented with the highest mean value of defects. The groups with and without polishing did not statistically differ from themselves. The finishing procedures can interfere positively or negatively on the regularity of finish line. Best preparations were those who maintained a tip of the same format that the preparation was performed (Diamond and Ultrasound tip). |