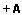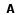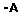Resumo: O haplótipo 46/1 do gene JAK2 foi recentemente descrito como um fator de risco importante para o desenvolvimento da neoplasias mieloproliferativas crônicas, tanto positivas como negativas para a mutação JAK2 V617F. O alelo G é caracterizado pelo polimorfismo de um único nucleotídeo, chamado JAK2 rs10974944, fazendo parte do haplótipo 46/1 do gene JAK2. O objetivo deste estudo foi verificar a associação entre a presença do haplótipo 46/1 do gene JAK2, representado pelo alelo G, e o desenvolvimento de neoplasias mieloproliferativas crônicas BCR-ABL negativas em nossa população. Sangue e amostras provenientes de swabs oral foram obtidos de 56 pacientes, atendidos em dois hospitais regionais, previamente diagnosticados como tendo neoplasias mieloproliferativas crônicas BCR-ABL negativas. Amostras de sangue de 90 doadores de sangue, provenientes do hemocentro local, foram utilizados como controle. Após a extração de DNA da amostra, a presença do alelo G foi pesquisada por genotipagem através da técnica de PCR-RFLP nas amostras provenientes de pacientes e controles. A frequência do alelo G foi significativamente maior em pacientes com neoplasias mieloproliferativas crônicas (p=0.0001; OR=2.674; 95% CI=1.630-4.385) quando comparado aos controles. Em concordância com os dados previamente descritos na literatura, a presença do haplótipo 46/1 do gene JAK2, representada pela presença do alelo G, mostrou-se como um importante fator predisponente ao desenvolvimento de neoplasias mieloproliferativas crônicas em nossa população.
Abstract: The JAK2 46/1 haplotype has recently been described as a major contributor factor to the development of myeloproliferative neoplasm either positive or negative for the JAK2 V617F mutation. The G allele of a specific single nucleotide polymorphism, called JAK2 rs10974944, is part of the JAK2 46/1 haplotype. The aim of this study is to verify the association between the presence of the JAK2 46/1 haplotype, represented by the G allele, and the development of BCR-ABL negative chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms in our population. Blood and oral mucosa swabs samples were obtained from 56 patients, from two local Brazilian hospitals, previously diagnosed as having BCR-ABL negative chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood samples from 90 local blood donors were used as controls. The presence of the G allele was accessed using a PCR-RFLP assay after DNA sample extraction. The presence of the G allele was strongly associated with the presence of BCR-ABL negative chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms (p=0.0001; OR=2.674; 95% CI=1.630-4.385) in the studied population. In agreement with previous reports, the JAK2 46/1 haplotype, represented here by the presence of the G allele, is an important predisposing factor in the oncogenetic development of these neoplasms in our population. |